Evaluación del efecto antiparasitario de las nanoparticulas de plata contra Trypanosoma cruzi in vitro
Palabras clave:
Trypanosoma cruzi, Chagas, AgNP, in vitro, plataResumen
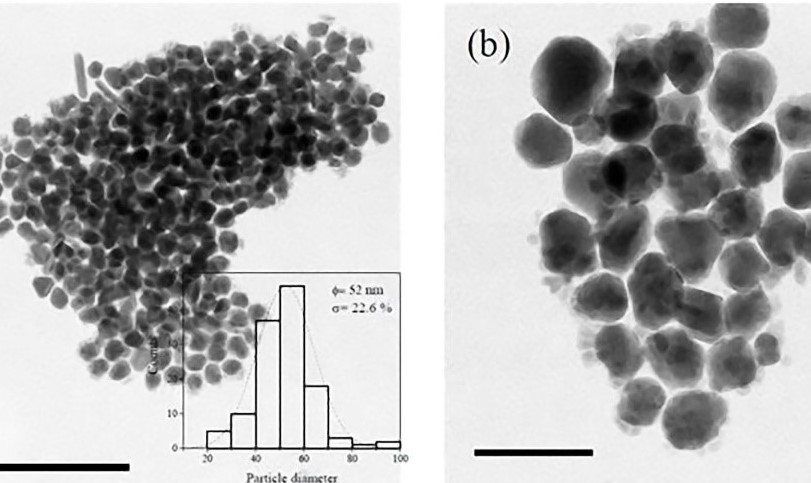
La tripanosomiasis Americana es una de las enfermedades tropicales desatendidas a nivel mundial, y es causada por el protozoario hemoflagelado Trypanosoma cruzi (Tc). Actualmente, los fármacos anti-Tc son limitados y no hay vacuna disponible. El objetivo de esta investigación fue evaluar el efecto de las nanopartículas de plata (AgNPs) contra los tripomastigotes de las cepas Sylvio X10/4 (TcI) y Esmeraldo (TcII). Las AgNPs se obtuvieron por el método de reducción y se les realizó una caracterización estructural. La actividad citotóxica de las AgNPs (actividad anti-Tc) se determinó mediante el cálculo de los valores de la mitad de la concentración inhibitoria máxima (IC50) en las células HaCaT y en los parásitos. Las AgNPs no mostraron citotoxicidad contra las células HaCaT en los valores de IC50 probadas en los parásitos, y la IC50 calculada en los tripomastigotes fue de 4.05 µg/ml y de 6.16 µg/ml en las cepas TcI y TcII respectivamente. Las AgNPs fueron más activas contra las dos cepas de Trypanosoma cruzi, que el nifurtimox (400 µg/ml) in vitro. Estos resultados sientan las bases para la evaluación mayor de las AgNPs, por investigar su potencial quimioterapéutico para combatir la infección por T. cruzi en modelos animales.
http://dx.doi.org/10.21929/abavet2023.15
e2022-64
Citas
ADEYEMI OS, Murata Y, Sugi T, Kato K. 2017. Inorganic nanoparticles kill Toxoplasma gondii via changes in redox status and mitochondrial membrane potential. International Journal of Nanomedicine. 12: 1647–1661. ISSN: 1176-9114.
https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S122178
ADIBHESAMI M, Ahmadi M, Farshid AA, Sarrafzadeh-Rezaei F, Dalir-Naghadeh B. 2017. Effects of silver nanoparticles on Staphylococcus aureus contaminated open wounds healing in mice: An experimental study. Veterinary Research Forum. 8(1): 23-28. ISSN: 2008-8140. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5413307/
ALLAHVERDIYEV AM, Abamor ES, Bagirova M, Ustundag CB, Kaya C, Kaya F. Rafailovich M. 2011. Antileishmanial effect of silver nanoparticles and their enhanced antiparasitic activity under ultraviolet light. International Journal of Nanomedicine. 6:2705. ISSN: 1176-9114. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S23883
APARICIO-BURGOS JE, Zepeda-Escobar, JA, de Oca-Jimenez, RM, Estrada-Franco, JG, Barbabosa-Pliego, A, Ochoa-García, L, Alejandre-Aguilar R, Rivas N, Peñuelas-Rivas, G, Val-Arreola M, Shivali Gupta, Salazar-García F, Garg NJ, Vázquez-Chagoyán JC. 2015. Immune protection against Trypanosoma cruzi induced by TcVac4 in a canine model. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 9(4): e0003625. ISSN: 1935-2735. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0003625
ATTARDE SS, Pandit, SV. 2020. Anticancer potential of nanogold conjugated toxin GNP-NN-32 from Naja naja venom. Journal of Venomous Animals and Toxins including Tropical Diseases. 26. ISSN: 1678-9199. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-9199-JVATITD-2019-0047
BAIOCCO P, Ilari, A, Ceci, P, Orsini, S, Gramiccia, M, Muccio TD, Colotti G. 2011. Inhibitory effect of silver nanoparticles on trypanothione reductase activity and Leishmania infantum proliferation. ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 2(3): 230-233. ISSN: 1948-5875. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/ml1002629
BARILE FA, Arjun, S, Hopkinson, D. 1993. In vitro cytotoxicity testing: biological and statistical significance. Toxicology In Vitro. 7(2):111-116. ISSN: 0887-2333. https://doi.org/10.1016/0887-2333(93)90120-T
BRITO TK, Viana, RLS, Moreno, CJG, da Silva Barbosa, J, de Sousa, JFL, de Medeiros, MJC, Rocha, HAO. 2020. Synthesis of silver nanoparticle employing corn cob xylan as a reducing agent with anti-Trypanosoma cruzi activity. International Journal of Nanomedicine. 15: 965-979. ISSN: 1176-9114. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S216386
CHAVES GC, Arrieche MAS, Rode J, Mechali D, Reis, PO, Stobbaerts, A, Girón AE, Nora, RI. 2017. Estimating demand for anti-Chagas drugs: a contribution for access in Latin America/Estimacion de la demanda de medicamentos antichagasicos: una contribucion para el acceso en America Latina/Estimativa da demanda de medicamentos antichagasicos: uma contribuicao para o acesso na America Latina. Revista Panamericana de Salud Pública. 41(8):1-8. ISSN: 1680 5348. https://www.scielosp.org/pdf/rpsp/2017.v41/e45/es
CHEN L, Wu, M, Jiang, S, Zhang, Y, Li, R, Yongbo L, Lin L, Gang W, Ying L, Liming X, Liming X. 2019. Skin toxicity assessment of silver nanoparticles in a 3D epidermal model compared to 2D keratinocytes. International Journal of Nanomedicine. 14:9707-9719. ISSN: 1176-9114. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S225451
COLANTONIO LD, Prado N, Segura EL, Sosa ES. 2016. Electrocardiographic abnormalities and treatment with benznidazole among children with chronic infection by Trypanosoma cruzi: a retrospective cohort study. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 10(5): e0004651. ISSN: 1935-2735. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0004651
DANKOVICH TA, Gray DG. 2011. Bactericidal paper impregnated with silver nanoparticles for point-of-use water treatment. Environmental Science & Technology. 45(5): 1992-1998. ISSN: 1520-5851. https://doi.org/10.1021/es103302t
DUBAS ST, Kumlangdudsana P, Potiyaraj P. 2006. Layer-by-layer deposition of antimicrobial silver nanoparticles on textile fibers. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects. 289(1-3): 105-109. ISSN: 0927-7757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2006.04.012
DUBEY P, Matai, I, Kumar, SU, Sachdev, A, Bhushan, B, Gopinath P. 2015. Perturbation of cellular mechanistic system by silver nanoparticle toxicity: Cytotoxic, genotoxic and epigenetic potentials. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science. 221: 4-21. ISSN: 0001-8686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2015.02.007
EL-SAYED NM, Myler PJ, Bartholomeu DC, Nilsson D, Aggarwal G, Tran AN, Ghedin E, Worthey EA, Delcher AL, Blandin G, Westenberger GS, Caler E, Cerqueira GC, Branche C, Haas B, Anupama A, Arner E, Aslund L, Attipoe P, Bontempi E, Bringaud F, Burton P, Cadag E, Campbell DA, Carrington M, Crabtree J, Darban H, da Silveira JF, de Jong P, Edwards K, Englund PT, Fazelina G, Feldblyum T, Ferella M, Frasch AC, Gull K, Horn D, Hou L, Huang Y, Kindlund E, Klingbeil M, Kluge S, Koo H. 2005. The genome sequence of Trypanosoma cruzi, etiologic agent of Chagas disease. Science. 309(5733): 409-415. ISSN: 00368075. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1112631
GE L, Li Q, Wang M, Ouyang J, Li X, Xing MMQ. 2014. Nanosilver particles in medical applications: synthesis, performance, and toxicity. International Journal of Nanomedicine. 9: 2399-2407. ISSN: 1176-9114. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S55015
IBÁÑEZ-CERVANTES G, León-García G, Castro-Escarpulli G, Mancilla-Ramírez J, Victoria-Acosta G, Cureño-Díaz MA, Sosa-Hernández O, Bello-López JM. 2018. Evolution of incidence and geographical distribution of Chagas disease in Mexico during a decade (2007–2016). Epidemiology & Infection. 147:1-7. ISSN: 1469-4409. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0950268818002984
JAMES TN, Rossi MA, Yamamoto S. 2005. Postmortem studies of the intertruncal plexus and cardiac conduction system from patients with Chagas disease who died suddenly. Progress in Cardiovascular Diseases. 47(4): 258-275. ISSN: 0033-0620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcad.2005.01.003
KIM JS, Kuk E, Yu KN, Kim JH, Park SJ, Lee HJ, Kim SH, Park YK, Park YH, Hwang CY, Kim YK, Lee YS, Jeong DH, Cho MH. 2007. Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology, and Medicine. 3(1): 95-101. ISSN: 1549-9634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2006.12.001
KOKURA S, Handa O, Takagi T, Ishikawa T, Naito Y, Yoshikawa, T. 2010. Silver nanoparticles as a safe preservative for use in cosmetics. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine. 6(4): 570-574. ISSN: 1549-9634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2009.12.002
LEE KS, El-Sayed MA. 2006. Gold and silver nanoparticles in sensing and imaging: sensitivity of plasmon response to size, shape, and metal composition. Journal of Physical Chemistry B. 110(39): 19220-19225. ISSN: 1520-5207. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp062536y
MAO BH, Tsai JC, Chen CW, Yan SJ, Wang YJ. 2016. Mechanisms of silver nanoparticle-induced toxicity and important role of autophagy. Nanotoxicology. 10(8): 1021-1040. ISSN: 1743-5404. https://doi.org/10.1080/17435390.2016.1189614
MEJIA AM, Hall BS, Taylor MC, Gómez-Palacio A, Wilkinson SR, Triana-Chávez O, Kelly JM. 2012. Benznidazole-resistance in Trypanosoma cruzi is a readily acquired trait that can arise independently in a single population. The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 206(2): 220-228. ISSN: 1537-6613. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jis331
MOLINA J, Martins-Filho, O, Brener, Z, Romanha, AJ, Loebenberg, D, Urbina, JA. 2000. Activities of the triazole derivative SCH 56592 (posaconazole) against drug-resistant strains of the protozoan parasite Trypanosoma (Schizotrypanum) cruzi in immunocompetent and immunosuppressed murine hosts. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 44(1): 150-155. ISSN: 1098-6596.
https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.44.1.150-155.2000
MORONES JR, Elechiguerra, JL, Camacho, A, Holt, K, Kouri, JB, Ramírez, JT, Yacaman, JM. 2005. The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology. 16(10): 2346. ISSN: 09574484. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/16/10/059
MOUSAVI SAA, Salari, S, Hadizadeh, S. 2015. Evaluation of antifungal effect of silver nanoparticles against Microsporum canis, Trichophyton mentagrophytes and Microsporum gypseum. Iran Journal of Biotechnology. 13(4): 38-42. ISSN: 1728-3043. https://doi.org/10.15171/ijb.1302
MULFINGER L, Solomon, SD, Bahadory, M, Jeyarajasingam, AV, Rutkowsky, SA, Boritz, C. 2007. Synthesis and study of silver nanoparticles. Journal of Chemical Education. 84(2): 322. ISSN: 00219584. https://doi.org/10.1021/ed084p322
PAL S, Tak, YK, Song, JM. 2007. Does the antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles depend on the shape of the nanoparticle? A study of the gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 73(6):1712-1720. ISSN: 1098-5336. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02218-06
PERDE-SCHREPLER M, Florea A, Brie I, Virag P, Fischer-Fodor E, Vâlcan A, Gurzău E, Lisencu C, Maniu A. 2019. Size-dependent cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in cochlear cells in vitro. Journal of Nanomaterials. e6090259. ISSN: 1687-4129. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6090259
ROLÓN M, Vega C, Escario JA, Gómez BA. 2006. Development of resazurin microtiter assay for drug sensibility testing of Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes. Parasitology Research. 99(2): 103-107. ISSN: 1432-1955. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-006-0126-y
SCALISE ML, Arrúa EC, Rial MS, Esteva MI, Salomon CJ, Fichera LE. 2016. Promising efficacy of benznidazole nanoparticles in acute Trypanosoma cruzi murine model: in-vitro and in-vivo studies. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. 95(2): 388-393. ISSN: 0002-9637. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.15-0889
SOLIMAN H, Elsayed A, Dyaa A. 2018. Antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles biosynthesised by Rhodotorula sp. strain ATL72. Egyptian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences. 5(3): 228-233. ISSN: 2314-808X. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejbas.2018.05.005
SUN Y, Xia Y. 2002. Shape-controlled synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles. Science. 298(5601): 2176-2179. ISSN: 00368075.
https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1077229
TOLEDO MJO, Bahia MT, Veloso VM, Carneiro CM, Machado-Coelho GLL, Alves CF, Martins HR, Cruz RE, Tafuri WL, Lana M. 2004. Effects of specific treatment on parasitological and histopathological parameters in mice infected with different Trypanosoma cruzi clonal genotypes. The Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 53(6):1045-1053. ISSN: 03057453. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkh224