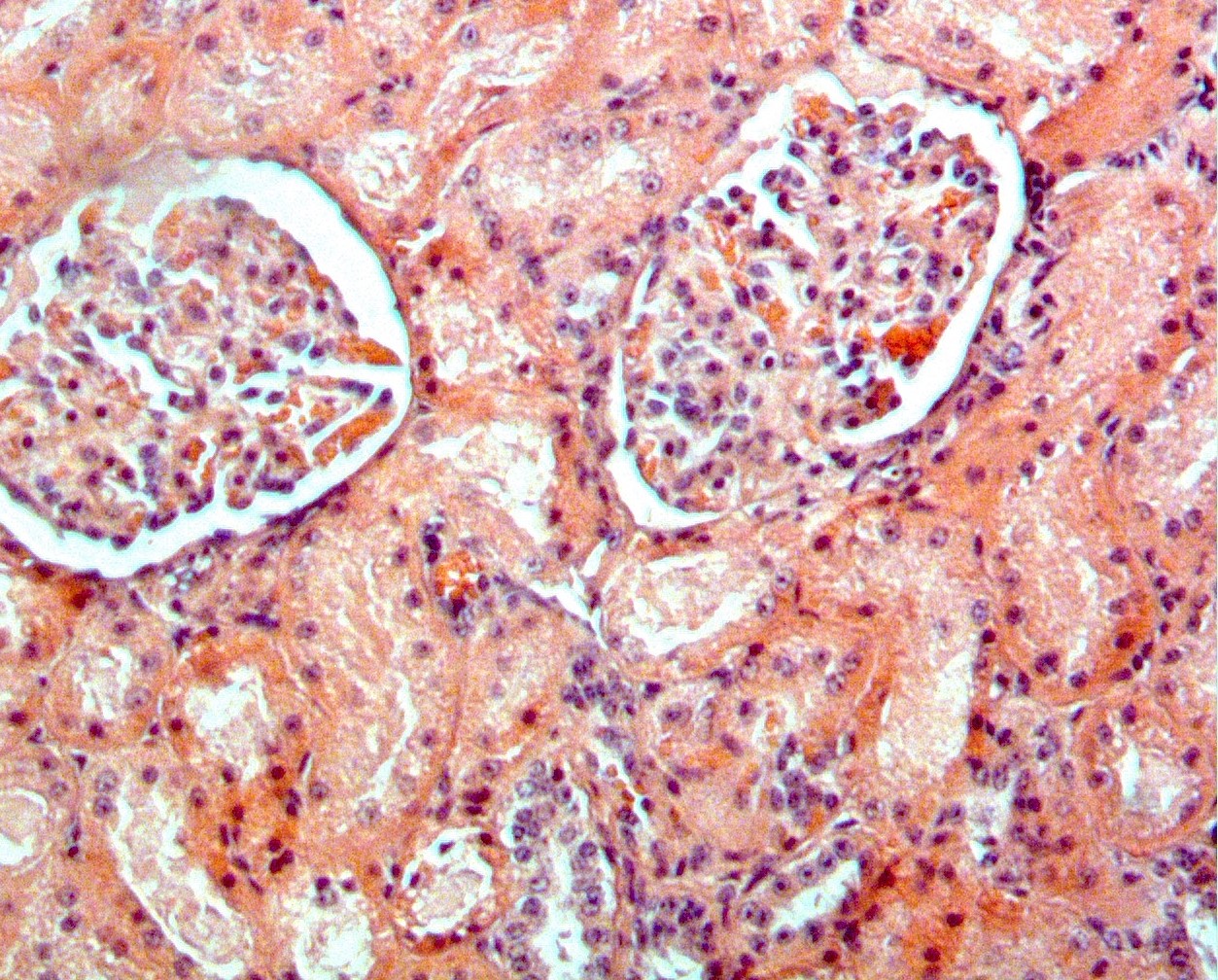
Amiloidose sistêmica AA: um problema potencial de saúde pública
Palavras-chave:
saúde pública, segurança alimentar, amiloidose, inflamação crônica, insuficiência renalResumo
O objetivo desta revisão é informar os profissionais de saúde animal sobre amiloidose sistêmica AA, um problema potencial de saúde pública pouco conhecido no México, que pode resultar do consumo de produtos de origem animal. O diagnóstico é difícil, pois os sinais clínicos dependem do tipo e da localização da amilóide, e sua fase terminal corresponde à insuficiência renal. Consiste no acúmulo de um material proteico extracelular que pode se originar de cerca de 37 proteínas normais em humanos e mais de 15 em outros mamíferos e aves aquáticas e terrestres. Possui uma estrutura fibrilar característica em um arranjo dobrado em β que a torna altamente resistente a agentes físico-químicos, dificultando sua remoção dos alimentos. Algumas amiloidoses, como a doença de Alzheimer em humanos e a disfunção cognitiva em cães, são localizadas, mas a amiloidose AA é sistêmica e há evidências naturais e experimentais de que ela pode ser transmitida intra e interespécies quando há entrada oral, intravenosa ou intraperitoneal de material amilóide em um indivíduo com uma doença inflamatória crônica pré-existente ou outros fatores de risco, como a obesidade, tornando-a um problema potencial de saúde pública.
http://dx.doi.org/10.21929/abavet2022.11 e2021-22.
Referências
ANDREI M, Wang JC. 2019. Cutaneous light chain amyloidosis with multiple myeloma: A concise review. Hematology/oncology and stem cell therapy.12(2):71–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hemonc.2018.09.003
BENSON MD, Buxbaum JN, Eisenberg DS, Merlini G, Saraiva M, Sekijima Y, Sipe JD, Westermark P. 2018. Amyloid nomenclature 2018: recommendations by the International Society of Amyloidosis (ISA) nomenclature committee. Amyloid: the international journal of experimental and clinical investigation: the official journal of the International Society of Amyloidosis. 25(4):215–219. https://doi.org/10.1080/13506129.2018.1549825
BIANCO C, Sánchez-Cordón PJ, Verin R, Godinho A, Weyer U, Lesellier S, Spiropoulos J, Floyd T, Everest D, Núñez A. 2020. Investigation into the Pathology of Idiopathic Systemic Amyloidosis in Four Captive Badgers (Meles meles). Journal of comparative pathology.176:128–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcpa.2020.02.012
BLANCAS-MEJÍA LM, Ramirez-Alvarado M. 2013. Systemic amyloidoses. Annual review of biochemistry. 82:745–774. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-072611-130030
BLANCHARD JL, Baskin GB, Watson EA. 1986. Generalized amyloidosis in rhesus monkeys. Veterinary pathology. 23(4): 425–430.
https://doi.org/10.1177/030098588602300412
BLANK N, Hegenbart U, Lohse P, Beimler J, Röcken C, Ho AD, Lorenz HM, Schönland SO. 2015. Risk factors for AA amyloidosis in Germany. Amyloid. 22(1): 1–7.
https://doi.org/10.3109/13506129.2014.980942
BLANK N, Hegenbart U, Dietrich S, Brune M, Beimler J, Röcken C, Müller-Tidow C, Lorenz HM, Schönland SO. 2018. Obesity is a significant susceptibility factor for idiopathic AA amyloidosis. Amyloid. 25(1):37–45. https://doi.org/10.1080/13506129.2018.1429391
BOBYLEV AG, Fadeev RS, Bobyleva LG, Kobyakova MI, Shlyapnikov YM, Popov DV, Vikhlyantsev IM. 2021. Amyloid Aggregates of Smooth-Muscle Titin Impair Cell Adhesion. International journal of molecular sciences. 22(9):4579.
https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094579
BREILLAT P, Pourcher V, Deshayes S, Buob D, Cez A, Michel P A, Boffa J J, Langlois V, Grateau G, Georgin-Lavialle S. 2021. AA Amyloidosis in the Course of HIV Infection: A Report of 19 Cases Including 4 New French Cases and a Comprehensive Review of Literature. Nephron. 145(6): 675–683. https://doi.org/10.1159/000516982
BRUNGER AF, Nienhuis H, Bijzet J, Hazenberg B. 2020. Causes of AA amyloidosis: a systematic review. Amyloid. 27(1): 1–12.
https://doi.org/10.1080/13506129.2019.1693359
CONASIDA (Consejo Nacional para la prevención y control del SIDA). 2021. Sistema de vigilancia epidemiológica de VIH. Informe histórico Día mundial VIH 2021.
https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/attachment/file/685220/VIH-Sida__D_a_Mundial_2021.pdf
COOPER C, Bilbao J E, Said S, Alkhateeb H, Bizet J, Elfar A, Davalos O, Meza AT, Hernandez G T. 2013. Serum amyloid A renal amyloidosis in a chronic subcutaneous ("skin popping") heroin user. Journal of Nephropatholy. 2(3): 196–200.
https://doi.org/10.12860/JNP.2013.31
D'SOUZA A, Theis JD, Vrana JA, Dogan A. 2014. Pharmaceutical amyloidosis associated with subcutaneous insulin and enfuvirtide administration. Amyloid.21(2): 71–75.
https://doi.org/10.3109/13506129.2013.876984
EISENBERG D, Jucker M. 2012. The amyloid state of proteins in human diseases. Cell.148(6):1188–1203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.02.022
ENCODAT (Encuesta Nacional de consumo de drogas, alcohol y tabaco). 2016. Encuesta nacional de consumo de drogas, alcohol y tabaco 2016-2017. Pp.1. https://www.gob.mx/cms/uploads/ATTACHMENT/file/234856/CONSUMO_DE_DROGAS.pdf
FLORES RODRÍGUEZ J, Rivera Franco MM, Apodaca Cruz Á, Saldaña Montaño MC, Urbalejo Ceniceros VI, Meneses García A, Herrera Gómez A, Perez Camargo DA, Sevilla González ML. 2019. Incidence and characteristics of metabolic syndrome in patients of the National Cancer Institute of Mexico. Nutrición hospitalaria. 36 (6):1296–1299. https://dx.doi.org/10.20960/nh.02395
FLORES-TREVIÑO S, Rodríguez-Noriega E, Garza-González E, González-Díaz E, Esparza-Ahumada S, Escobedo-Sánchez R, Pérez-Gómez HR,León-Garnica G, Morfín-Otero R. 2019. Clinical predictors of drug-resistant tuberculosis in Mexico. PLoS ONE 14(8): e0220946. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0220946
FRAME NM, Gursky O. 2017. Structure of serum amyloid A suggests a mechanism for selective lipoprotein binding and functions: SAA as a hub in macromolecular interaction networks. Amyloid. 24(1): 13-14 https://doi.org/10.1080/13506129.2016.1270930
FRANKLIN AD, Schmidt-Küntzel A, Terio KA, Marker LL, Crosier AE. 2016. Serum Amyloid A Protein Concentration in Blood is Influenced by Genetic Differences in the Cheetah (Acinonyx jubatus). The Journal of heredity. 107(2): 115–121. https://doi.org/10.1093/jhered/esv089
GAFFNEY PM, Witte C, Clifford DL, Imai DM, O'Brien TD, Trejo M, Liberta F, Annamalai K, Fändrich M, Masliah E, Munson L, Sigurdson CJ. 2016. Systemic Amyloid A Amyloidosis in Island Foxes (Urocyon littoralis): Severity and Risk Factors. Veterinary pathology. 53(3):637–647. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300985815604725
GALINDO SRM, Peniche OG, Herrera RJ, Gryzbowski E. 2013. Estimación de la prevalencia de artritis reumatoide en México. Value in health. ISPOR 16TH Annual European Congress Research abstracts. 16 (7): A719.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jval.2013.08.2235
GURSKY O. 2020. Structural Basis for Vital Function and Malfunction of Serum Amyloid A: an Acute-Phase Protein that Wears Hydrophobicity on Its Sleeve. Current atherosclerosis reports. 22(11): 69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11883-020-00888-y
GREUNZ EM, Lemberger K, Catinaud J, Chenet B, Linke RP, Bräsen JH, Schmitz J, Bertelsen MF. 2020. AMYLOIDOSIS IN CARACALS (CARACAL CARACAL). Journal of zoo and wildlife medicine. 51(1):202–209. https://doi.org/10.1638/2019-0005
GRUYS E. 2004. Protein folding pathology in domestic animals. Journal of Zhejiang University-Science. 5(10):1226–1238. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2004.1226
HAMPEL MR, Kinne J, Wernery U, Pospischil A, Kellermann J, Linke RP. 2009. Increasing fatal AA amyloidosis in hunting falcons and how to identify the risk: a report from the United Arab Emirates. Amyloid.16(3):122–132.
https://doi.org/10.1080/13506120903090759
HASHIMOTO M, Rockenstein E, Crews L, Masliah E. 2003. Role of protein aggregation in mitochondrial dysfunction and neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. Neuromolecular medicine. 4:21–35. https://doi.org/10.1385/NMM:4:1-2:21
HUKKANEN RR, Liggitt HD, Anderson DM, Kelley ST 2006. Detection of systemic amyloidosis in the pig-tailed macaque (Macaca nemestrina). Comparative medicine. 56(2): 119–127. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16639979/
INEGI (Instituto Nacional de Estadística, Geografía e Informática). 2020. Comunicado de prensa número 24/21. 25 de enero de 2021. Pp. 2.
https://www.inegi.org.mx/contenidos/saladeprensa/boletines/2021/EstSociodemo/ResultCenso2020_Nal.pdf
JANSSON DS, Bröjer C, Neimanis A, Mörner T, Murphy,CL, Otman F, Westermark P. 2018. Post mortem findings and their relation to AA amyloidosis in free-ranging Herring gulls (Larus argentatus). PloS ONE.13(3): e0193265.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0193265
JUCKER M, Walker LC. 2013. Self-propagation of pathogenic protein aggregates in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature: 501(7465):45–51.
https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12481
JUNG O, Haack HS, Buettner M, Betz C, Stephan C, Gruetzmacher P, Amann K, Bickel M. 2012. Renal AA-amyloidosis in intravenous drug users--a role for HIV-infection?. BMC nephrology.13: 151. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2369-13-151
KADOTA A, Iwaide S, Miyazaki S, Mitsui I, Machida N, Murakami T. 2020. Pathology and Proteomics-Based Diagnosis of Localized Light-Chain Amyloidosis in Dogs and Cats.Veterinary pathology. 57(5): 658–665. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300985820934113
KHELLAF G, Benziane A, Kaci L, Benabadji M. 2022. AA renal amyloidosis: Clinical observations over 20 years. Clinical nephrology. 97:167-172.
https://doi.org/10.5414/CN110577
KLEIN A, Radespiel U, Felmy F, Brezina T, Ciurkiewicz M, Schmitz J, Bräsen JH, Linke R, P, Reinartz S, Distl O, Beineke A. 2021. AA-amyloidosis in captive northern tree shrews (Tupaia belangeri). Veterinary pathology. https://doi.org/10.1177/03009858211066847
LACHMANN HJ, Goodman HJ, Gilbertson JA, Gallimore JR, Sabin CA, Gillmore JD, Hawkins PN. 2007. Natural history and outcome in systemic AA amyloidosis.The New England journal of medicine. 356(23): 2361–2371.
https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa070265
LARSEN CP, Beggs ML, Wilson JD, Lathrop SL. 2016. Prevalence and organ distribution of leukocyte chemotactic factor 2 amyloidosis (ALECT2) among decedents in New Mexico.Amyloid.23(2): 119–123. https://doi.org/10.3109/13506129.2016.1145110
LEUNG ET, Raboin MJ, McKelvey J, Graham A, Lewis A, Prongay K, Cohen AM, Vinson A. 2019. Modelling disease risk for amyloid A (AA) amyloidosis in non-human primates using machine learning. Amyloid. 26(3): 139–147.
https://doi.org/10.1080/13506129.2019.1625038
LIN X, Watanabe K, Kuragano M, Tokuraku K. 2021. Aggregation of Mouse Serum Amyloid A Protein Was Promoted by Amyloid-Enhancing Factors with the More Genetically Homologous Serum Amyloid A. International journal of molecular sciences. 22(3):1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031036
LUDLAGE E, Murphy CL, Davern SM, Solomon A, Weiss DT, Glenn-Smith D, Dworkin S, Mansfield KG. 2005. Systemic AA amyloidosis in the common marmoset.Veterinary pathology. 42(2):117–124. https://doi.org/10.1354/vp.42-2-117
LUNDMARK K, Westermark G T, Olsén A, Westermark P. 2005. Protein fibrils in nature can enhance amyloid protein A amyloidosis in mice: Cross-seeding as a disease mechanism.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America.102 (17): 6098–6102. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0501814102
LUNDMARK K, Vahdat Shariatpanahi A, Westermark GT. 2013. Depletion of spleen macrophages delays AA amyloid development: a study performed in the rapid mouse model of AA amyloidosis. PloS ONE. 8(11):e79104.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0079104
MAJI SK, Perrin MH, Sawaya MR, Jessberger S, Vadodaria K, Rissman RA, Singru PS, Nilsson KP, Simon R, Schubert D, Eisenberg D, Rivier J, Sawchenko P, Vale W,Riek R. 2009. Functional amyloids as natural storage of peptide hormones in pituitary secretory granules. Science. 325(5938): 328–332. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1173155
MARTIN DJ, Randles EG, Ramirez-Alvarado M. 2010. Fibril structure and fibrillogenesis. En: Gertz M.A. y Rajkumar S.J. Amyloidosis: Diagnosis and treatment 1ª edición. Humana Press. Pp.2. ISBN: 978-1-60761-631-3. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60761-631-3
MARTINEZ ME, Zimmerman D, Seeley KE, Zhang L, Bapodra P, Cianciolo RE. 2019. Systemic amyloidosis in a population of pronghorn antelope (Antilocapra americana). Journal of zoo and wildlife medicine. 50(1):147–158.
https://doi.org/10.1638/2018-0055
MENDOZA JM, Peev V, Ponce MA, Thomas DB, Nayer A. 2013. Amyloid A amyloidosis with subcutaneous drug abuse. Journal of renal injury prevention. 3(1): 11–16. https://doi.org/10.12861/jrip.2014.06
MOLLEE P, Renaut P, Gottlieb D, Goodman H. 2014. How to diagnose amyloidosis. Internal medicine journal. 44(1): 7–17. https://doi.org/10.1111/imj.12288
MURAKAMI T, Inoshima Y, Watanabe K, Kobayashi Y, Matsui T, Kurazono H, Ishiguro N. 2011. Pathogenesis of experimental amyloid protein A amyloidosis in sore hocks-affected rabbits. Amyloid.18(3):112–118. https://doi.org/10.3109/13506129.2011.582901
MURAKAMI T, Muhammad N, Inoshima Y, Yanai T, Goryo M, Ishiguro N. 2013. Experimental induction and oral transmission of avian AA amyloidosis in vaccinated white hens. Amyloid. 20 (2): 80–85. https://doi.org/10.3109/13506129.2013.783474
MURAKAMI T, Ishiguro N, Higuchi K. 2014. Transmission of systemic AA amyloidosis in animals. Veterinary pathology. 51(2):363–371.
https://doi.org/10.1177/0300985813511128
MURAKAMI T, Inoshima Y, Ishiguro N. 2015. Systemic AA amyloidosis as a prion-like disorder.Virus research. 207: 76–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virusres.2014.12.019
NAKAGUN S, Watanabe K, Matsuishi, T., Kobayashi, M., Kobayashi, Y. 2019. Surveillance of amyloidosis in stranded and bycaught cetaceans off Hokkaido, Japan. The Journal of veterinary medical science. 81(6): 897–902. https://doi.org/10.1292/jvms.18-0706
NAKAGUN S, Watanabe K, Tajima Y, Yamada TK, Kobayashi Y. 2020. Systemic Amyloid A Amyloidosis in Stejneger's Beaked Whales (Mesoplodon stejnegeri).Veterinary pathology. 57 (3):437–444. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300985820914079
NAKANO Y, Madarame H. 2020. Systemic amyloid A (AA) amyloidosis in the Bengalese finch (Lonchura striata var. domestica).The Journal of veterinary medical science. 82 (10): 1484–1487. https://doi.org/10.1292/jvms.20-0365
NIEWOLD TA, Murphy CL, Toussaint MJ, Solomon A, Gruys E. 2005. Chemical typing of porcine systemic amyloid as AA-amyloid. Amyloid.12(3): 164–166.
https://doi.org/10.1080/13506120500231806
OGAWA M, Shintani-Domoto Y, Nagashima Y, Ode KL, Sato A, Shimizu Y, Ohashi K, Roehrl M, Ushiku T, Ueda HR, Fukayama M. 2020. Mass spectrometry-based absolute quantification of amyloid proteins in pathology tissue specimens: Merits and limitations.PloS ONE.15 (7): e0235143.https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0235143
OLSSON M, Tintle L, Kierczak M, Perloski M, Tonomura N, Lundquist A, Murén E, Fels M, Tengvall K, Pielberg G, Dufaure de Citres C, Dorso L, Abadie J, Hanson J, Thomas A, Leegwater P, Hedhammar Å, Lindblad-Toh K, Meadows J. R. 2013. Thorough investigation of a canine autoinflammatory disease (AID) confirms one main risk locus and suggests a modifier locus for amyloidosis. PloS ONE. 8(10): e75242.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0075242
OVELGÖNNE JH, Landman WJ, Gruys E, Gielkens AL, Peeters BP. 2001. Identical amyloid precursor proteins in two breeds of chickens which differ in susceptibility to develop amyloid arthropathy. Amyloid. 8 (1): 41–51.
https://doi.org/10.3109/13506120108993813
PALTRINIERI S, Sironi G, Giori L, Faverzani S, Longeri M. 2015. Changes in serum and urine SAA concentrations and qualitative and quantitative proteinuria in Abyssinian cats with familial amyloidosis: a five-year longitudinal study (2009-2014). Journal of veterinary internal medicine. 29(2): 505–512. https://doi.org/10.1111/jvim.12561
PAPENDICK RE, Munson L, O'Brien TD, Johnson KH.1997. Systemic AA amyloidosis in captive cheetahs (Acinonyx jubatus). Veterinary pathology. 34(6): 549–556.
https://doi.org/10.1177/030098589703400602
PICKEN MM. 2020. The Pathology of Amyloidosis in Classification: A Review. Acta haematologica.143 (4): 322–334. https://doi.org/10.1159/000506696
REAL DE ASÚA D, Costa R, Galván JM, Filigheddu MT, Trujillo D, Cadiñanos, J. 2014. Systemic AA amyloidosis: epidemiology, diagnosis, and management. Clinical epidemiology. 6: 369–377. https://doi.org/10.2147/CLEP.S39981
RICE KA, Chen ES, Metcalf Pate KA, Hutchinson EK, Adams RJ. 2013. Diagnosis of amyloidosis and differentiation from chronic, idiopathic enterocolitis in rhesus (Macaca mulatta) and pig-tailed (M. nemestrina) macaques. Comparative medicine. 63(3): 262–271.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23759529/
RISING A, Cederlund E, Palmberg C, Uhlhorn H, Gaunitz S, Nordling K, Ågren E, Ihse E, Westermark GT, Tjernberg L, Jörnvall H, Johansson J, Westermark P. 2017. Systemic AA amyloidosis in the red fox (Vulpes vulpes). Protein science. 26(11): 2312–2318. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.3264
RISING A, Gherardi P, Chen G, Johansson J, Oskarsson ME, Westermark GT, Westermark P. 2021. AA amyloid in human food chain is a possible biohazard. Scientific reports.11(1): 21069. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-00588-w
ROMANI M, Sorrentino V, Oh CM, Li H, de Lima TI, Zhang H, Shong M, Auwerx J. 2021. NAD+ boosting reduces age-associated amyloidosis and restores mitochondrial homeostasis in muscle. Cell reports. 34(3): 108660.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108660
RUBEL MS, Fedotov SA, Grizel AV, Sopova JV, Malikova OA, Chernoff YO, Rubel AA. 2020. Functional Mammalian Amyloids and Amyloid-Like Proteins. Life. 10 (9):156.
https://doi.org/10.3390/life10090156
SACK GH., Jr 2018. Serum amyloid A - a review. Molecular medicine. 24 (1):46. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10020-018-0047-0
SCARPIONI R, Ricardi M, Albertazzi V. 2016. Secondary amyloidosis in autoinflammatory diseases and the role of inflammation in renal damage. World journal of nephrology. 5 (1): 66–75. https://doi.org/10.5527/wjn.v5.i1.66
SEGEV G, Cowgill LD, Jessen S, Berkowitz A, Mohr CF, Aroch I. 2012. Renal amyloidosis in dogs: a retrospective study of 91 cases with comparison of the disease between Shar-Pei and non-Shar-Pei dogs. Journal of veterinary internal medicine. 26(2): 259–268. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1939-1676.2011.00878.x
SIKORA J, Kmochová T, Mušálková D, Pohludka M, Přikryl P, Hartmannová H, Hodaňová K, Trešlová H, Nosková L, Mrázová L, Stránecký V, Lunová M, Jirsa M, Honsová E, Dasari S, McPhail ED, Leung N, Živná M, Bleyer A J, Rychlík I, Kmoch S. 2021. A mutation in the SAA1 promoter causes hereditary amyloid A amyloidosis. Kidney international. 101(2): 349-359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2021.09.007
SILVA-HERNÁNDEZ L, Horga Hernández A, Valls Carbó A, Guerrero Sola A, Montalvo-Moraleda MT, Galán Dávila L. 2020. «Red flags» en pacientes con polineuropatía amiloidótica familiar relacionada con transtiretina (hATTR) en el momento del diagnóstico en un área no endémica de España. Neurología. S0213-4853 (20): 30212-7.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nrl.2020.06.009
SIPE JD, Benson MD, Buxbaum JN, Ikeda S, Merlini G, Saraiva MJ, Westermark P. Nomenclature Committee of the International Society of Amyloidosis .2012. Amyloid fibril protein nomenclature: 2012 recommendations from the Nomenclature Committee of the International Society of Amyloidosis. Amyloid.19(4): 167–170.
https://doi.org/10.3109/13506129.2012.734345
SIPE JD, Benson MD, Buxbaum JN, Ikeda SI, Merlini G, Saraiva MJ, Westermark P. 2016. Amyloid fibril proteins and amyloidosis: chemical identification and clinical classification International Society of Amyloidosis 2016 Nomenclature Guidelines. Amyloid.23(4): 209–213. https://doi.org/10.1080/13506129.2016.1257986
SØRBY R, Espenes A, Landsverk T, Westermark G. 2008. Rapid induction of experimental AA amyloidosis in mink by intravenous injection of amyloid enhancing factor. Amyloid.15(1): 20–28. https://doi.org/10.1080/13506120701815332
TAMURA Y, Chambers JK, Neo S, Goto-Koshino Y, Takagi S, Uneyama M, Uchida, K, Hisasue M. 2020. Primary duodenal plasmacytoma with associated primary (amyloid light-chain) amyloidosis in a cat. Journal of Feline Medicine and Surgery open reports.6(2): 2055116920957194. https://doi.org/10.1177/2055116920957194
TANAKA S, Dan C, Kawano H, Omoto M, Ishihara T. 2008. Pathological study on amyloidosis in Cygnus olor (mute swan) and other waterfowl. Medical molecular morphology. 41(2): 99–108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00795-008-0401-3
TOJO K, Tokuda T, Hoshii Y, Fu X, Higuchi K, Matsui T, Kametani F, Ikeda S. 2005. Unexpectedly high incidence of visceral AA-amyloidosis in slaughtered cattle in Japan. Amyloid.12(2): 103–108. https://doi.org/10.1080/13506120500107097
VAN DER HEIJDEN RA, Bijzet J, Meijers WC, Yakala GK, Kleemann R, Nguyen TQ, de Boer RA, Schalkwijk CG, Hazenberg BP, Tietge UJ, Heeringa P. 2015. Obesity-induced chronic inflammation in high fat diet challenged C57BL/6J mice is associated with acceleration of age-dependent renal amyloidosis. Scientific reports. 5: 16474.
https://doi.org/10.1038/srep16474
VAN DER HILST JC. 2011. Recent insights into the pathogenesis of type AA amyloidosis. The Scientific World Journal. 11: 641–650.
https://doi.org/10.1100/tsw.2011.64
VAN DER LINDE-SIPMAN JS, Niewold TA, Tooten PC, de Neijs-Backer M, Gruys E.1997. Generalized AA-amyloidosis in Siamese and Oriental cats. Veterinary immunology and immunopathology. 56 (1-2): 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-2427(96)05717-0
VAHDAT SHARIAT PANAHI A, Hultman P, Öllinger K, Westermark GT, Lundmark K. 2019. Lipid membranes accelerate amyloid formation in the mouse model of AA amyloidosis. Amyloid. 26(1): 34–44. https://doi.org/10.1080/13506129.2019.1576606
WEKELL P, Karlsson A, Fasth A, Berg S. 2016. Familjär medelhavsfeber - viktig sjukdom i en globaliserad värld - Särskilt vanlig hos personer från östra Medelhavsområdet [Familial Mediterranean fever – an important disease in a globalised world]. Lakartidningen. 113: DZFY. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27551868/
WESTERMARK P, Andersson A, Westermark GT. 2011. Islet amyloid polypeptide, islet amyloid, and diabetes mellitus. Physiological reviews. 91(3):795–826.
https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00042.2009
WESTERMARK GT, Fändrich M, Lundmark K, Westermark P. 2018. Noncerebral Amyloidoses: Aspects on Seeding, Cross-Seeding, and Transmission. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in medicine. 8(1): a024323.
https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a024323
ZHANG B, Une Y, Fu X, Yan J, Ge F, Yao J, Sawashita J, Mori M, Tomozawa H, Kametani, F, Higuchi K. 2008. Fecal transmission of AA amyloidosis in the cheetah contributes to high incidence of disease. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 105(20): 7263–7268.