Frequência de Campylobacter fetus em bovinos reprodutores na região central de Tamaulipas, México
Palavras-chave:
Campylobacter fetus veneralis, touros, sêmen, lavagem prepucial, MéxicoResumo
A campilobacteriose genital bovina (CGB) é uma doença infecciosa contagiosa que afeta o gado. A doença
é considerada uma doença de notificação obrigatória e está incluída na lista B de doenças de animais
terrestres, de acordo com a Organização Mundial de Saúde Animal (OMSA). Em ruminantes, foi
demonstrado que o Campylobacter fetus subsp. fetus afeta (Cff) o sistema entérico, especialmente o
intestino, e é uma das principais causas de infertilidade e aborto em bovinos, ovinos e caprinos. A doença
foi relatada em vários países do mundo. No México, a presença desse patógeno tem sido pouco estudada;
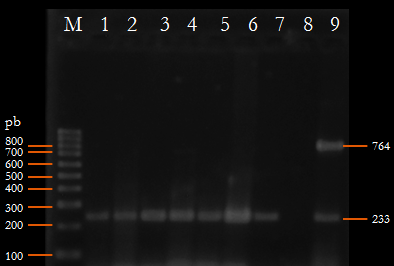
neste estudo, a existência de Campylobacter fetus subsp. veneralis (CFv) em touros da área central de
Tamaulipas, México, foi comprovada pela técnica de PCR e sequenciamento do produto amplificado, o que
representa o primeiro relato desse patógeno por métodos moleculares nesse país.
e2022-57
Referências
ADHIKARI P, Antala D, Bhandari B, Mohamed K, Egoryan G, Stake JJ, Friedman H. 2022. A Case of Campylobacter Fetus Subspecies Fetus Systemic Infection. Cureus Journal of Medical Science. 14:e23963. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.23963
ALTSCHUL SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. Journal of Molecular Biology. 215:403-10. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2
BARAJAS JA. 2013. Seroepidemiología de Campylobacter fetus subes. venerealis en ganado bovino en el trópico de México. Congreso Nacional de Buiatría XXXVII. https://www.expresionesveterinarias.com/2018/09/seroepidemiologia-de-campylobacter.html
CAGNOLI CI, Chiapparrone ML, Cacciato CS, Rodríguez MG, Aller JF, Catena MDC. 2020. Effects of Campylobacter fetus on bull sperm quality. Microbial Pathogenesis. 149:1-5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104486
CAMPOS-MÚZQUEZ LG, Méndez ET, Arellano B, Martínez D. 2019. Campylobacter fetus is Internalized by Bovine Endometrial Epithelial Cells. Polish Journal of Microbiology. 68:217-224. https://doi.org/10.33073/pjm-2019-022
CAMPOS-MÚZQUEZ LG, Méndez ET, Palacios N, Martínez D. 2021. Campylobacter fetus Induced Proinflammatory Response in Bovine Endometrial Epithelial Cells. Polish Journal of Microbiology. 70:99-106. https://doi.org/10.33073/pjm-2021-009
CHABAN B, Chu S, Hendrick S, Waldner C, Hill JE. 2012. Evaluation of a Campylobacter fetus subspecies venerealis real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction for direct analysis of bovine preputial samples. Canadian Journal of Veterinary Research. 76:166-73. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3384278/
CHIAPPARRONE ML, Morán PE, Echevarría HM, Soto P, Paolicchi FA, Catena M. 2014. Campylobacter fetus subsp. venerealis adhesion to MDBK cells. Revista Argentina de Microbiología. 46:269-70. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0325-7541(14)70081-1
CHUKWU MO, Luther KA, Ubomba-Jaswa E, Obi L, Dewar JB. 2019. Characterization and Phylogenetic Analysis of Campylobacter Species Isolated from Paediatric Stool and Water Samples in the Northwest Province, South Africa. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.16:2205.
https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16122205
CLUNE T, Bruce M, Glanville E, Campbeñ AS, Lockwood A, Hancock S, Thompson AN, Beetson S, Brookes D, Trengove C. 2022. Seropositivity to Campylobacter and association with abortion and lamb mortality in maiden ewes from Western Australia, South Australia and Victoria. Australian Veterinary Journal. 10.1111/avj.13173. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1111/avj.13173
DELPIAZZO R, Barcellos M, Barros S, Betancor L, Fraga M, Gil J, Iraola G, Morsella C, Paolicchi F, Pérez R, Riet-Correa F, Sanguinetti M, Silva A, Silva S, Calleros L. 2021. Accurate and fast identification of Campylobacter fetus in bulls by real-time PCR targeting a 16S rRNA gene sequence. Veterinary and Animal Science. 11:100163.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vas.2020.100163
DORSCH MA, Francia ME, Tana LR, González C, Cabrera A, Calleros L, Sanguinetti M, Barcellos M, Zarantonelli L, Ciuffo C, Maya L, Castells M, Mirazo S, Silva S, Rabaza A, Caffarena RD, Doncel B, Aráoz V, Matto C, Armendano I, Giannitti F. 2022. Diagnostic Investigation of 100 Cases of Abortion in Sheep in Uruguay: 2015-2021. Frontiers in Veterinary Science. 9:904786. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2022.904786
FERNÁNDEZ R, Lorenzo-Vizcaya AM, Bustillo M, Fernández R. 2022. Campylobacter fetus meningitis and subdural empyema. Enfermedades infecciosas y microbiologia clinica (English ed.), 40:212–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eimce.2022.02.005
FERREIRA F, Oliveira P, Bastos F, Paula M, Leite M, Pereira L. 2002. Evaluation of direct fluorescent antibody test for the diagnosis of bovine genital campylobacteriosis. Rev Latinoam Microbiol. 44:118–23. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17063594/
GROFF A, Kirinus J, Sá e SM, Manchado G, Mateus MC, Agueda V. 2010. Polymerase chain reaction for the diagnosis of bovine genital campylobacteriosis. Pesquisa Veterinaria Brasileira. 30:1031-1035. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-736X2010001200005
HOQUE N, Islam SK, Uddin MN, Arif M, Haque AK, Neogi SB, Hossain MM, Yamasaki S, Kabir SM. 2021. Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Molecular Detection of Campylobacter in Farmed Cattle of Selected Districts in Bangladesh. Pathogens. 10:313. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10030313
HUM S, Quinn K, Brunner J, Slw O. 1997 Evaluation of a PCR assay for identification and differentiation of Campylobacter fetus subspecies. Australian Veterinary Journal. 75:827–831. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-0813.1997.tb15665.x
IRAOLA G, Hernández M, Calleros L, Paolicchi F, Silveyra S, Velilla A, Carretto L, Rodríguez E, Pérez R. 2012. Application of a multiplex PCR assay for Campylobacter fetus detection and subspecies differentiation in uncultured samples of aborted bovine fetuses. Journal of Veterinary Science. 13:371-6
https://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2012.13.4.371
IRAOLA G, Pérez R, Betancor L, Marandino A, Morsella C, Méndez A, Paolicchi F, Piccirillo A, Tomás G, Velilla A, Calleros L. 2016. A novel real-time PCR assay for quantitative detection of Campylobacter fetus based on ribosomal sequences. BMC Veterinary Research. Dec12:286. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-016-0913-3
LI X, Tang H, Xu Z, Tang H, Fan Z, Jiao X, Huang J. 2022. Prevalence and characteristics of Campylobacter from the genital tract of primates and ruminants in Eastern China. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases, 10.1111/tbed.14524. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1111/tbed.14524
LÚCIO ÉC, Barros MR, Mota RA, de Cássia Carvalho Maia R, Pinheiro JW. 2019. Identification of Campylobacter fetus subsp. venerealis virulence genes in cervical mucus from cows. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology. 50:1133-1137.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s42770-019-00127-w
LYNCH CT, Buttimer C, Epping L, O'connor J, Walsh N, McCarthy C, O'brien D, Vaughan C, Semmler T, Bolton D, Coffey A, Lucey B. 2022. Phenotypic and genetic analyses of two Campylobacter fetus isolates from a patient with relapsed prosthetic valve endocarditis. Pathogens and Disease. 79:ftab055. https://doi.org/10.1093/femspd/ftab055
MSHELIA GD, Amin JD, Egwu GO, Woldehiwet Z, Murray RD. 2012. The prevalence of bovine venereal campylobacteriosis in cattle herds in the Lake Chad basin of Nigeria. Tropical Animal Health and Production. 44:1487-1489. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-012-0092-6
SILVEIRA CDS, Fraga M, Giannitti F, Macías-Rioseco M, Riet-Correa F. 2018. Diagnosis of Bovine Genital Campylobacteriosis in South America. Frontiers in Veterinary Science. 5:321. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2018.00321
TSHIPAMBA ME, Akinola SA, Ngoma L, Mwanza M. 2020. Genome Sequence of Campylobacter fetus subsp. venerealis NW_ED23, Isolated from Bovine Sheath Wash. Microbiology Resource Announcements. 9:e00854-20.